What’s the Difference: No-Fault vs. Tort Car Insurance
The difference between no-fault vs. tort car insurance laws is that in no-fault states, drivers are responsible for damages to their own vehicles and sometimes their own medical bills regardless of who caused the accident.
Read more Secured with SHA-256 Encryption




Table of Contents
Table of Contents


Insurance Feature Writer
Rachel Bodine graduated from college with a BA in English. She has since worked as a Feature Writer in the insurance industry and gained a deep knowledge of state and countrywide insurance laws and rates. Her research and writing focus on helping readers understand their insurance coverage and how to find savings. Her expert advice on insurance has been featured on sites like PhotoEnforced, All...
Rachel Bodine


Licensed Insurance Agent
Michelle Robbins has been a licensed insurance agent for over 13 years. Her career began in the real estate industry, supporting local realtors with Title Insurance. After several years, Michelle shifted to real estate home warranty insurance, where she managed a territory of over 100 miles of real estate professionals. Later, Agent Robbins obtained more licensing and experience serving families a...
Michelle Robbins
Updated March 2025
What’s the difference between no-fault vs. tort car insurance? If you’ve recently renewed a car insurance policy, you may have experienced sticker shock based on an increase in the cost of your premium. When insurers issue rates, there is always a reason. And despite the myth that auto insurers are not regulated, each state regulates the companies that sell car insurance, and they also have strict guidelines as to how much they sell it for.
No-Fault vs. Tort Car Insurance
Because car insurance regulations vary by state, your location significantly influences policy premiums. There are two fundamental auto insurance systems: ‘no-fault’ and ‘at-fault’ (commonly known as tort liability auto insurance). Understanding these differing systems, each governed by specific state guidelines, can be complex and crucial when considering if tort car insurance is necessary.
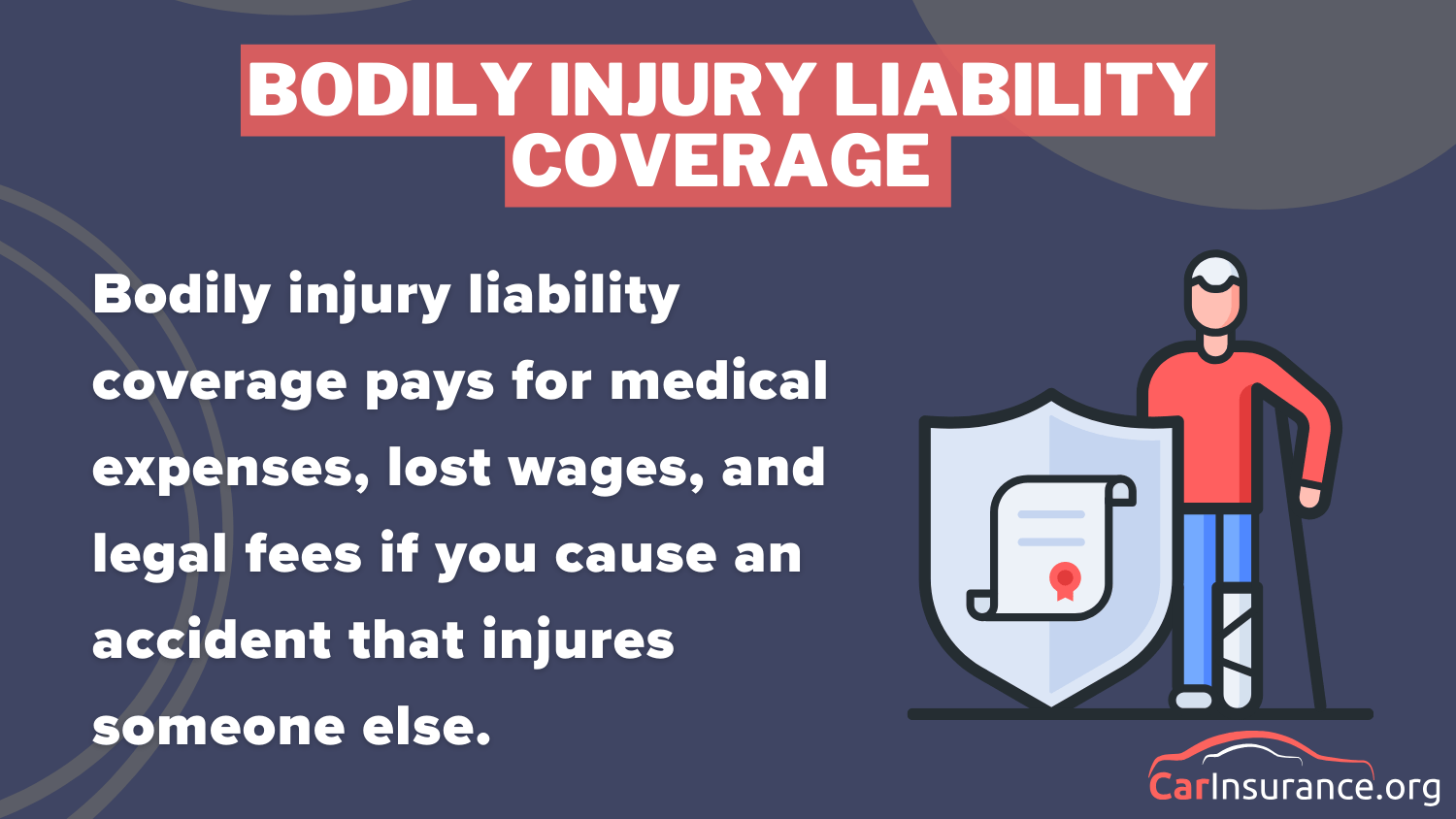
The typical form of no-fault coverage is Personal Injury Protection which covers medical expenses, loss of income, and wages for the driver and the passengers, unlike bodily injury liability coverage which covers medical costs in case you have caused the accident. It does not cover property damage liability or car repairs. PIP coverage ensures that all drivers get care for their injuries and compensation for the cost without identifying who caused the accident.
For those who live in states with a no-fault system (twelve states have no-fault laws in place – Florida, Hawaii, Kansas, Kentucky, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, New Jersey, New York, North Dakota, Pennsylvania, Utah, and the District of Columbia) the difference in automobile tort states can be overwhelming. And the same can be said of those who drive in tort states who have no idea how no-fault systems work.
In a no-fault state, drivers are accountable for their own vehicle damages and, at times, their own medical expenses, even in accidents involving another driver. This responsibility applies regardless of who caused the accident. Additionally, drivers in no-fault states typically need to have Personal Injury Protection (PIP) coverage. This system ensures that all drivers receive medical care and compensation for costs without determining fault. This setup contributes to the benefits of no-fault insurance, affects car insurance cost differences by state, and contrasts with the concept of full coverage insurance.
In the context of no-fault vs. at-fault insurance, the courts in no-fault states generally do not prioritize determining fault in accidents. Typically, they avoid assigning blame unless cases involve significant medical bills or property damage. In such rare instances, the court system may be prompted to ascertain fault. This illustrates the relationship between tort law and insurance practices, where fault determination varies based on the insurance system in place.
Free Insurance Comparison
Compare Quotes From Top Companies and Save
Secured with SHA-256 Encryption
Pros and Cons of No-Fault and Auto Tort Insurance
Claimed benefits of no-fault insurance:
- Efficient payment of claims
- Reduced load on courts, with no need to hire attorneys
- Insurance premiums should be lowered
Claimed negatives of no-fault insurance:
- There are specified limits on when you can sue
- No incentive to be a good driver, other than policy premiums
- Insurance fraud is a pervasive issue in no-fault states
- Evidence points to no savings on insurance premiums, and in many cases, premiums have proven to be higher
Tort states and the automobile tort system of insurance for personal injury claims are more common. In a tort or “at-fault” state, the driver who is responsible for an accident must pay the costs of an accident or at least a proportional amount of the fees incurred by the other driver – tort systems often assign blame as a percentage, rather than singling out an individual driver. The damages related to an accident are paid out through the negligent party’s liability insurance coverage.
Many people living in at-fault states choose to purchase uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage because it offers protection from damages caused by someone who does not have liability insurance or has very low coverage limits on their policy. Medical Payments coverage is also popular in these states, as it offers additional protection in the case of injuries from automobile accidents, making it less likely a person will have to deal with the hassle of finding a personal injury attorney and filing a lawsuit. Most auto insurance companies offer these forms of coverage in at-fault states, but keep in mind any optional coverages added to your auto policy will increase your insurance premium.
Each state has its own methods for determining the at-fault driver and the percentage of fault assigned to each driver, along with different systems for covering minor accident injuries. In automobile tort cases, particularly in torts involving motor vehicle accidents, insurance claims may not be paid until after fault is established, which can sometimes occur following a lawsuit.
No-Fault vs. Tort Car Insurance: Which is better?
While we won’t delve into the debate over which system is superior, it’s clear that proponents of no-fault car insurance highlight the significant court costs that both drivers and insurance companies face in at-fault states. On the other hand, supporters of tort systems argue that fault-based insurance is inherently fairer. They argue against penalizing drivers for accidents they didn’t cause, which is a fundamental difference between tort and no-fault states.
Another interesting fact is that since the introduction of the no-fault insurance concept, 24 states have enacted (and many have repealed) such systems. And one final note about no-fault vs. tort-based systems. Three states – Kentucky, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania – have mixed systems that allow a policyholder to choose which system they have: traditional tort or no-fault. These choice-based systems require all policyholders to select between the two at the time a policy is issued or renewed. Once this occurs, a policyholder cannot convert to the other system without a full policy rewrite. In Kentucky and New Jersey, consumers who do not make a choice will be assigned a no-fault option by default; and in Pennsylvania, the tort option is the default for those who do not specify a choice. Drivers who select limited tort insurance reduce their ability to sue for damages related to auto accidents.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is automobile tort?
Automobile tort, or tort auto insurance, refers to a legal system in which fault and liability are established after a car accident. It typically involves one party seeking compensation from another for damages, depending on who was responsible. Unlike modified no-fault insurance, this system determines who is at fault to allocate financial responsibility for the accident.
What is liability without fault?
Liability without fault, often seen in no-fault insurance coverage, refers to situations where an individual can be legally held accountable for damages or injuries despite not intentionally causing harm. This concept is applicable in various legal scenarios, such as strict liability laws, and is common in no-fault auto insurance states.
What is no-fault automobile insurance?
In no-fault insurance states, the no-fault auto insurance system requires each party’s insurance provider to cover their own medical expenses and damages, regardless of who is at fault for the accident. This no-fault system is designed to simplify claims and minimize litigation.
What is no-fault coverage?
No-fault coverage pertains to insurance policies that offer benefits to policyholders irrespective of fault in an accident. This typically includes Personal Injury Protection (PIP) to cover medical expenses. Understanding the pros and cons of no-fault insurance is crucial, especially for those living in states with no-fault insurance laws.
What is the difference between no-fault and at-fault?
The difference between no-fault automobile insurance and at-fault or tort auto insurance coverage lies in how fault is assigned and claims are processed after an accident. With no-fault auto insurance, each party’s insurer covers their own damages, regardless of who caused the accident. Conversely, in tort driving states, the at-fault driver’s insurance is responsible for covering the other party’s damages. When seeking no-fault auto insurance quotes, it’s important to understand these distinctions.
What is tort coverage?
Tort insurance, also known as liability coverage in car accidents, pertains to insurance policies that protect against damages or injuries inflicted by the policyholder on another person or their property. This type of coverage is prevalent in states where fault is determined following an accident.
What is tort liability insurance?
Tort liability insurance provides coverage to the policyholder for claims related to damages or injuries they are responsible for in an accident, assisting in covering legal expenses and compensatory damages up to the policy’s specified limits. This type of insurance is particularly relevant in cases involving tort law and insurance.
What is the tort option in car insurance?
The tort option allows policyholders in certain states to choose between a traditional tort liability system or a no-fault system for their insurance coverage.
Which states are no-fault states for car insurance?
No-fault states for car insurance include Florida, Hawaii, Kansas, Kentucky, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, New Jersey, New York, North Dakota, Pennsylvania, Utah, and the District of Columbia.
What is one difference between a “tort” and “no fault” state?
One key difference is how insurance claims are handled. In tort states, fault is assigned, and the at-fault party’s insurance covers damages. In no-fault states, each party’s insurance covers their own damages regardless of fault.
What is car insurance?
What is no-fault insurance?
What is PIP insurance?
Why do drivers need liability coverage under a no-fault insurance system?
Is Alabama a no-fault state?
Is Iowa a no-fault state for car insurance?
Is Rhode Island (RI) a no-fault state?
Is Vermont a no-fault state?
What is the difference between full tort and limited tort in New Jersey?
Get a FREE Quote in Minutes
Insurance rates change constantly — we help you stay ahead by making it easy to compare top options and save.